
Ransomware and malware have unfortunately become commonplace occurrences in businesses of all sizes. Cyber criminals will go to tremendous lengths to subject companies to malicious malware attacks. Although hackers can utilize a number of tactics to infiltrate organizational databases—phishing attacks have become one of the most prevalent methods of bypassing network security systems. Phishing attacks currently account for over 80% of reported security incidents.
“Phishing has evolved into a massive problem that expands far beyond the traditional email bait and hook,” says Phil Hochmuth, Program Vice President of Enterprise Mobility at IDC.
The widespread prevalence of phishing attacks and schemes means that any type of business may be subjected to harmful malware. Utilizing a number of creative tactics, phishing emails are sent out at a rate of 3.4 billion per day.
Using social engineering techniques to deceive and defraud users—unknowing company employees are often lured by cyber criminals using communication tactics falling under the guise of trusted sources. Criminals often attempt to deceive users using deceptive methods—appearing as social websites, banking personnel, or internal high-level executives.
Although the prominence of phishing attacks continues to wreak havoc on organizations—companies can take action to ward off dubious online criminals.
What are Phishing Attacks?
Phishing uses social engineering attacks to penetrate sensitive data systems. Cybercriminals use phishing to deceive victims and gain access to login credentials, credit card numbers, and other forms of personal information.
Recipients generally receive emails that appear to originate from legitimate sources. Oftentimes these falsified emails contain malicious links that send harmful malware into computers and servers. Clicking on links often leads to the installation of malware, operation system malfunction, or the dissemination of sensitive information.
Individuals opening phishing emails may become victims of unauthorized purchases, bank fraud, or even identity theft. On the corporate side, phishing may be used to bypass security systems or obtain privileged information.
Phishing emails generally contain one or more of the following elements:
- Using urgency, over-friendly messages, or fear-mongering tactics to encourage user participation
- Promises of gifts, money, or other items
- Personal information widely available on the internet from social media sites or online public domains
Companies should protect their valuable online assets by minimizing the risk of phishing email attacks.
How Can You Protect Your Company?
Phishing attacks can result in substantial financial losses for companies. Businesses must do everything in their power to minimize the risk of potential attacks. Users must remain vigilant when it comes to opening emails from unknown sources.
Executives should employ defensive security strategies to help protect employees from phishing attacks. Leaders should train staff on cyber dangers, communicate safety precautions, and develop cyber policies to help protect users.
Employees should be frequently updated on phishing and malware topics to help prevent complacency. Sending simulated phishing messages to staff can be useful for educational purposes. Employees that fail tests should be given additional training resources to prevent future occurrences.
Standardized phishing awareness training should be given on an annual basis to keep employees updated and alert. Although phishing techniques were originally disseminated via email, today cybercriminals can employ attacks through text messages, social media, and other messaging applications.
Here some steps employees can use to identify potential phishing attacks:
- Look out for spelling and grammatical errors. Spelling mistakes attempt to fool algorithms by giving off the appearance of credibility. Pay attention to detail and never open up unidentified emails.
- Verify the validity of links within emails. Many times emails contain URLs similar to reputable websites, but contain variations that are slightly off.
- Never give personal information. If an email requests personal data or information, it's likely a phishing email.
- Don’t download attachments. Many files contain hidden attachments that can download malicious software onto your computer.
Although many corporate office spaces utilize firewalls and virus protection strategies—remote employees may not have access to the same security tools from home. Employee negligence or ignorance can further contribute to higher risks of attack.
Can you Catch the Phish in the Following Examples?
Below are a few examples of recent phishing emails. Look through them and find out if you can locate the red flags to identify them as malware.
Email #1
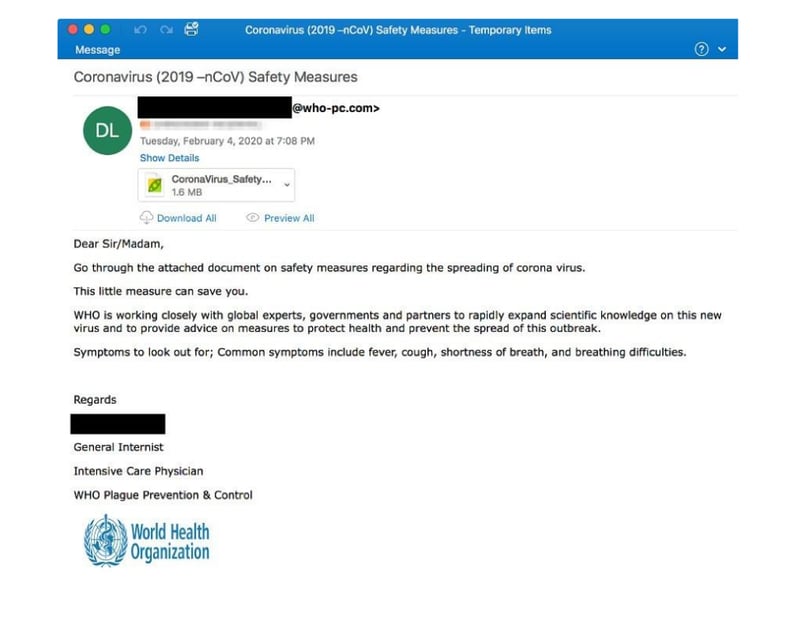
- Should be (COVID-19)
- WHO international origination email address should read: who.it
- Be suspicious of all attachments
- Bad grammar & repetition
- Plague Prevention & Control is not a legitimate division of WHO
- Warped logo
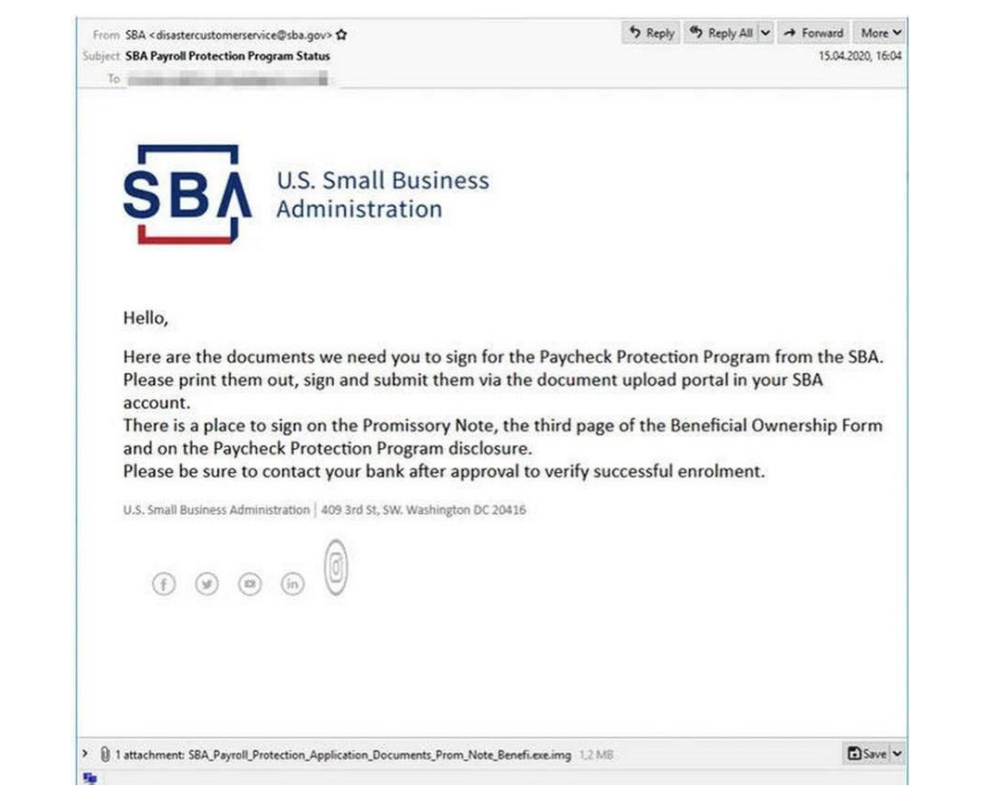
Email #2
Email #3
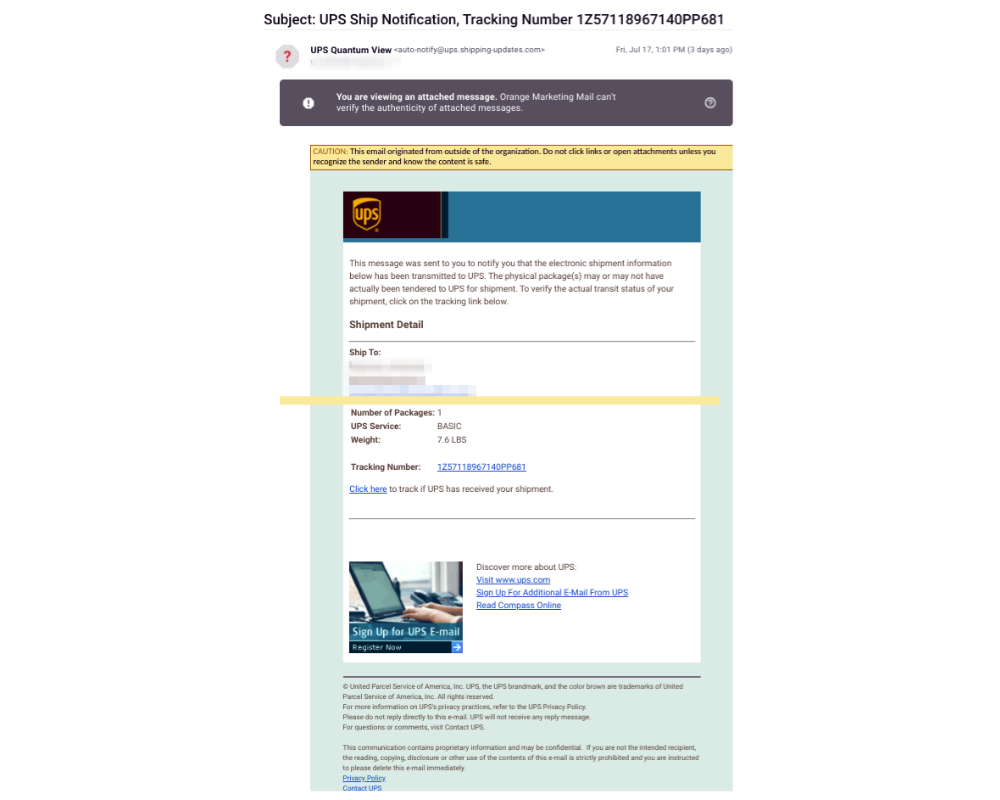
- Bad grammar – should be “UPS Shipping Notification”
- Origination mail address should be “ups.com”
- Ship to: not an address, only name and email address of the phished person
- All links on the page go to the same non-UPS site
- Copyright detail missing (year)
Let TBC Minimize the Risk of Phishing Attacks
Phishing has become one of the most common sources of cyber attacks. As organizations struggle to prevent malicious malware from impacting their businesses—leaders should develop strategies that aim to minimize the risk of potential attacks. That’s where TBC can help.
TBConsulting offers fully managed solutions that proactively monitor and assess digital environments. We’re able to determine risk, protect data, and create strategic surveillance approaches.
We help our clients protect their data while providing 24/7 security support. Our preventative measures allow us to take every step possible to safeguard against the risk of potential cyber attacks.
If you would like to learn more information about how TBC can manage your company’s security needs, feel free to reach out for a free 30 minute consultation. Don’t let your company become another statistic of phishing attacks.
.png)

